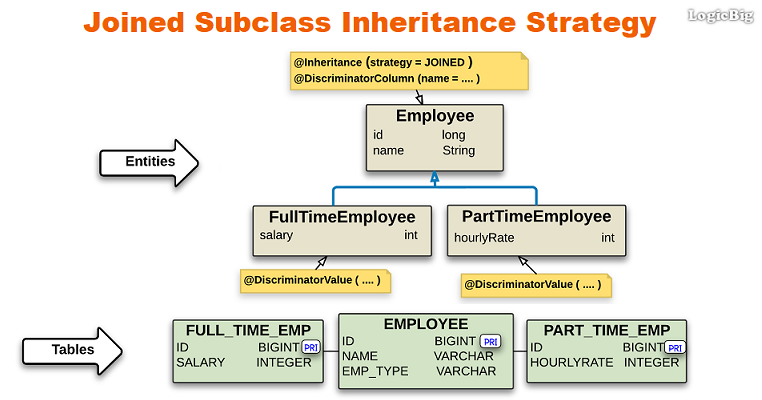
- In this strategy, the superclass and subclasses in a hierarchy are mapped to different individual tables.
- The tables corresponding to subclasses do not contain the field from the superclass, except for the @Id fields which are mapped to the primary key(s) of each table.
- The primary key column(s) of the subclass table serves as a foreign key to the primary key of the superclass table.
- The annotation @Inheritance is used on the root entity class with strategy =
InheritanceType.JOINED.
- @DiscriminatorColumn is used on the root entity class to specify the discriminator column attributes. Discriminator is a way to differentiate rows belonging to different subclasses in the root table.
- @DiscriminatorValue is used on each persistable subclass to specify a unique discriminator value.
- @Entity and other meta-data annotations are used on the root and subclasses as usual.
- @Id field should only be defined in the root class.
- The root class can be abstract or a concrete class.
- This strategy has the disadvantage of using one or more join queries to instantiate instances of a subclass. In deep class hierarchies, this may lead to unacceptable performance hit.
Example
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED)
@Entity
@DiscriminatorColumn(name = "EMP_TYPE")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private long id;
private String name;
.............
}
@Entity
@DiscriminatorValue("F")
@Table(name = "FULL_TIME_EMP")
public class FullTimeEmployee extends Employee {
private int salary;
.............
}
@Entity
@DiscriminatorValue("P")
@Table(name = "PART_TIME_EMP")
public class PartTimeEmployee extends Employee {
private int hourlyRate;
.............
}
public class ExampleMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory emf =
Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("example-unit");
try {
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
nativeQuery(em, "SHOW TABLES");
nativeQuery(em, "SHOW COLUMNS from EMPLOYEE");
nativeQuery(em, "SHOW COLUMNS from FULL_TIME_EMP");
nativeQuery(em, "SHOW COLUMNS from PART_TIME_EMP");
} finally {
emf.close();
}
}
.............
}'SHOW TABLES'
[EMPLOYEE, PUBLIC]
[FULL_TIME_EMP, PUBLIC]
[PART_TIME_EMP, PUBLIC]
'SHOW COLUMNS from EMPLOYEE'
[EMP_TYPE, VARCHAR(31), NO, , NULL]
[ID, BIGINT(19), NO, PRI, NULL]
[NAME, VARCHAR(255), YES, , NULL]
'SHOW COLUMNS from FULL_TIME_EMP'
[SALARY, INTEGER(10), NO, , NULL]
[ID, BIGINT(19), NO, PRI, NULL]
'SHOW COLUMNS from PART_TIME_EMP'
[HOURLYRATE, INTEGER(10), NO, , NULL]
[ID, BIGINT(19), NO, PRI, NULL]
A quick overview of the mapping:
Persisting and loading data
public class ExampleMain2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EntityManagerFactory emf =
Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("example-unit");
try {
persistEntities(emf);
runNativeQueries(emf);
loadEntities(emf);
} finally {
emf.close();
}
}
private static void persistEntities(EntityManagerFactory emf) throws Exception {
System.out.println("-- Persisting entities --");
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
FullTimeEmployee e1 = new FullTimeEmployee();
e1.setName("Sara");
e1.setSalary(100000);
System.out.println(e1);
PartTimeEmployee e2 = new PartTimeEmployee();
e2.setName("Robert");
e2.setHourlyRate(60);
System.out.println(e2);
em.getTransaction().begin();
em.persist(e1);
em.persist(e2);
em.getTransaction().commit();
em.close();
}
private static void runNativeQueries(EntityManagerFactory emf) {
System.out.println("-- Native queries --");
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
ExampleMain.nativeQuery(em, "Select * from Employee");
ExampleMain.nativeQuery(em, "Select * from FULL_TIME_EMP");
ExampleMain.nativeQuery(em, "Select * from PART_TIME_EMP");
}
private static void loadEntities(EntityManagerFactory emf) {
System.out.println("-- Loading entities --");
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
List<Employee> entityAList = em.createQuery("Select t from Employee t")
.getResultList();
entityAList.forEach(System.out::println);
em.close();
}
}-- Persisting entities --
FullTimeEmployee{id=0, name='Sara', salary=100000}
PartTimeEmployee{id=0, name='Robert', hourlyRate='60'}
-- Native queries --
'Select * from Employee'
[F, 1, Sara]
[P, 2, Robert]
'Select * from FULL_TIME_EMP'
[100000, 1]
'Select * from PART_TIME_EMP'
[60, 2]
-- Loading entities --
FullTimeEmployee{id=1, name='Sara', salary=100000}
PartTimeEmployee{id=2, name='Robert', hourlyRate='60'}
Example ProjectDependencies and Technologies Used: - h2 1.4.196: H2 Database Engine.
- hibernate-core 5.2.10.Final: The core O/RM functionality as provided by Hibernate.
Implements javax.persistence:javax.persistence-api version 2.1 - JDK 1.8
- Maven 3.3.9
|
|