When you place @Tag on a test class, that tag is automatically applied to:
- All test methods in that class.
- All nested test classes (@Nested).
- All test methods inside those nested classes.
In other words, class-level @Tag annotations propagate down to or are inherited by all methods defined within that class.
Example
In this example, we will show the use of @Tag on class level.
Using @Tag on class level
package com.logicbig.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Tag;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
@Tag("calc-test")
class ClassLevelTagUsageTest {
@Test
void primeNumberTest() {
assertEquals(2, 1 + 1);
}
@Test
void sumTest() {
assertTrue(true);
}
}
As seen above we used @Tag("calc-test") on class level, so this tag is actually applied to all methods in the class.
Another class using @Tag
package com.logicbig.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Tag;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
@Tag("integration")
class ClassLevelTagUsageTest2 {
@Test
void dbTransactionTest() {
assertTrue(true);
}
@Test
@Tag("staging")
void stagingTest() {
assertEquals(2, 1 + 1);
}
@Test
@Tag("calc-test")
void testFactorial(){
assertTrue(true);
}
}
In the above example, we used the following tags:
We applied @Tag("integration") at the class level, meaning all methods within the class automatically inherit this tag. We explicitly applied @Tag("staging") to the stagingTest() method. This means the stagingTest() method now has two tags: 'integration' (inherited) and 'staging' (explicit). We explicitly applied @Tag("calc-test") to the testFactorial() method. This means the testFactorial() method also has two tags: 'integration' (inherited) and 'calc-test' (explicit). (Note that we used the same tag 'calc-test' on the class level in the last example.)
Test Execution and Filtering (IntelliJ)
Using tag expression "calc-test"
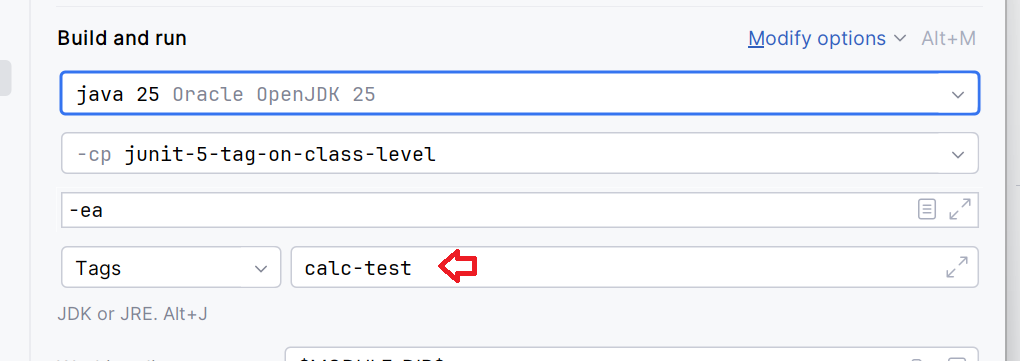
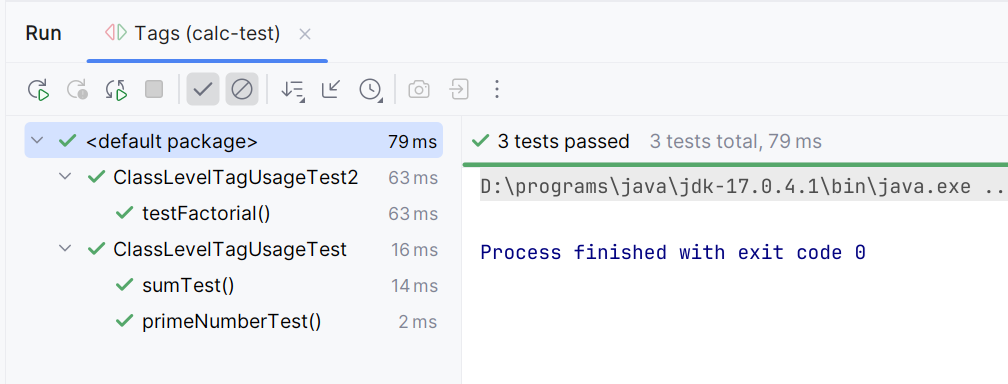
As seen above, the tag expression "calc-test" executed three methods: primeNumberTest(), sumTest(), and testFactorial(), as the first two inherit the tag from ClassLevelTagUsageTest and the last has the tag explicitly defined in ClassLevelTagUsageTest2.
Using tag expression "integration & staging"
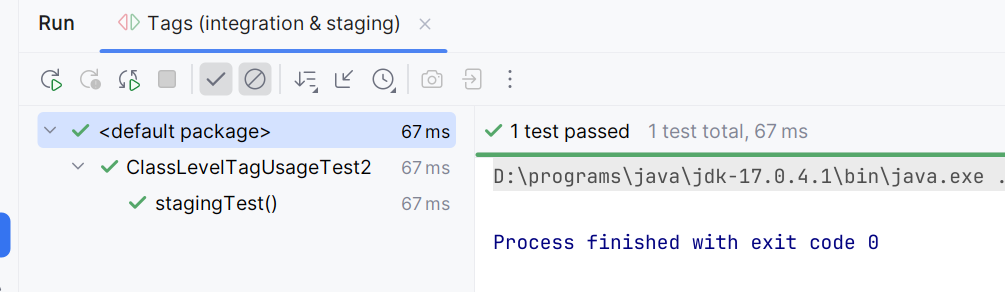
Outcomes of other tag expressions
integration & !calc-test
The tag expression "integration & !calc-test" will execute only dbTransactionTest() and stagingTest() from the second class, as they are tagged with integration but not with calc-test.
calc-test & integration
The tag expression "calc-test & integration" will execute only the testFactorial() method, as it is the single test that possesses both tags.
!staging
The tag expression "!staging" will execute all methods except stagingTest(), as the exclamation mark excludes any test explicitly tagged with staging.
calc-test | integration
This expression filters for tests that possess either the calc-test tag OR the integration tag (or both).
So this expression will execute all five test methods across both classes (primeNumberTest(), sumTest(), dbTransactionTest(), stagingTest(), and testFactorial()), as every test method in our example possesses at least one of these two tags through inheritance or explicit application.
Example ProjectDependencies and Technologies Used: - junit-jupiter-engine 6.0.1 (Module "junit-jupiter-engine" of JUnit)
Version Compatibility: 5.0.0 - 6.0.1 Version compatibilities of junit-jupiter-engine with this example:
- 5.0.0
- 5.0.1
- 5.0.2
- 5.0.3
- 5.1.0
- 5.1.1
- 5.2.0
- 5.3.0
- 5.3.1
- 5.3.2
- 5.4.0
- 5.4.1
- 5.4.2
- 5.5.0
- 5.5.1
- 5.5.2
- 5.6.0
- 5.6.1
- 5.6.2
- 5.6.3
- 5.7.0
- 5.7.1
- 5.7.2
- 5.8.0
- 5.8.1
- 5.8.2
- 5.9.0
- 5.9.1
- 5.9.2
- 5.9.3
- 5.10.0
- 5.10.1
- 5.10.2
- 5.10.3
- 5.10.4
- 5.10.5
- 5.11.0
- 5.11.1
- 5.11.2
- 5.11.3
- 5.11.4
- 5.12.0
- 5.12.1
- 5.12.2
- 5.13.0
- 5.13.1
- 5.13.2
- 5.13.3
- 5.13.4
- 5.14.0
- 5.14.1
- 6.0.0
- 6.0.1
Versions in green have been tested.
- JDK 25
- Maven 3.9.11
|