In a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system, three key components (Embedding Model, Vector Store, and LLM) work together to provide accurate, context-aware responses. As of early 2026, these components have become highly specialized and agentic.
1. Embedding Model
Purpose: Converts text (documents, queries) into numerical vectors (embeddings) that capture deep semantic meaning. In 2026, these models are increasingly multimodal and instruction-aware.
Example Vendors and Models (2026 Landscape):
- OpenAI: text-embedding-4-large, text-embedding-3-large
- Google: EmbeddingGemma-300M (On-device), text-embedding-005, text-multilingual-embedding-002
- Voyage AI: voyage-3.5, voyage-code-3 (Specialized for Enterprise)
- Cohere: embed-v4.0 (Multimodal & Multilingual)
- Open Source: Qwen3-Embedding, BGE-M3, Nomic Embed Text V2 (MoE Architecture)
The embedding model creates a vector representation of knowledge. Recent 2026 trends include Instruction-aware embeddings where you can tell the model how to embed based on the task (e.g., "Embed this for medical retrieval").
2. Vector Store (Vector Database)
Purpose: Stores and indexes embedding vectors, enabling efficient similarity search. In 2026, these are the "Long-term Memory" for AI Agents.
Example Vendors (2026 Landscape):
- Pinecone: Known for its high-performance serverless architecture and low-latency search.
- Milvus: The leading open-source choice for massive-scale distributed vector search.
- Weaviate: Specialized in hybrid search and integrated multimodal capabilities.
- Chroma: Optimized for developer experience and rapid prototyping.
- Enterprise SQL/NoSQL: pgvector (PostgreSQL), MongoDB Atlas Vector Search, and Snowflake Cortex.
Modern vector stores now support Hybrid Retrieval (combining semantic vector search with keyword/BM25 search) and Graph-enhanced RAG to understand relationships between data points.
3. Large Language Model (LLM)
Purpose: The "Brain" that takes the retrieved context and the user's question to generate a final, grounded response. In 2026, LLMs have shifted toward Reasoning and Planning.
Example Tier 1 Models (2026 Landscape):
- Google Gemini 3: Gemini 3 Pro (High reasoning), Gemini 3 Flash (Ultra-speed), and Gemini 3 Deep Think.
- OpenAI: GPT-5.2, GPT-5.1 (High-intelligence "o-series" reasoning models).
- Anthropic: Claude 4.5 Opus, Claude 4 Sonnet.
- Meta (Open Weights): Llama 4 (405B), Llama 4 (70B).
The 2026 generation of LLMs features Agentic Behavior, meaning they don't just answer—they can use tools to verify facts or browse the web if the retrieved context is insufficient.
How They Work Together in RAG
Architecture Flow:
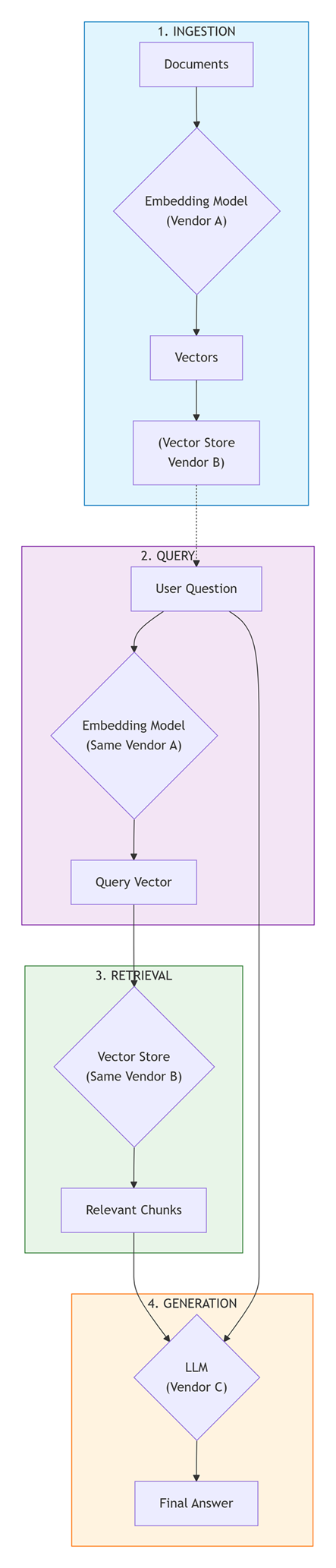
RAG Orchestrators (The Glue)
To build a RAG system, you need a framework to connect these three parts. Below are the leaders in 2026:
Java Orchestrators
- LangChain4j: The standard for Java/Spring Boot developers, providing
AiServices for declarative RAG.
- Spring AI: Deeply integrated with the Spring ecosystem for enterprise-grade deployments.
- Semantic Kernel (Java): Microsoft’s framework focused on enterprise "kernel" orchestration.
Non-Java Orchestrators
- LangChain (Python/JS): The industry leader with the most integrations (v2.0+).
- Dify: A popular visual workflow editor for building complex agentic RAG.
- LlamaIndex: Specialized for data-centric RAG and complex document parsing.
- Google Antigravity: Google’s new 2026 platform for building autonomous agents using Gemini 3.
Summary: In 2026, the best RAG systems use a Gemini 3 or GPT-5 class model for reasoning, a specialized Voyage or Qwen3 embedding model for retrieval, and a serverless vector store like Pinecone or Milvus for scale.
|
|